Analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) is necessary
because, while embedded systems deal with digital values, their surroundings
typically involve many analog signals such as, temperature, speed, pressure,
the output of a microphone, etc. They all need to be converted into digital
data before being processed by the microcontroller. Today, we will see how to
read an external analog signal using a PIC16F877a microcontroller, and display
the conversion output (a digital number) on a LCD. The input analog signal will
be a varying voltage between 0-5V derived using a potentiometer.
Microcontrollers have 5 inputs for 28 pin devices
and 8 inputs for 40/44 pin devices. It is a 10-bit ADC, ie the conversion of
analog signal results in corresponding 10-bit digital number. The positive and
negative reference voltage (+Vref and -Vref) of PIC ADC is software selectable,
which can be VDD, VSS, voltage at RA2 or RA3. This A/D Converter module can
also operate in sleep mode in which clock is derived from its internal RC
oscillator. Following points may help you to understand the concept of
reference voltages.
• When
the ADC input is -Vref, result will be 0000000000
• When
the ADC input is +Vref, result will be 1111111111
• Resolution
of ADC = (+Vref – -Vref)/(210 – 1), which is the minimum voltage required to
change the ADC result by one bit.
• Here
ADC Resolution = (5 – 0)/(1024 – 1) = 5/1023 = 0.004887V
• So,
if the input is 5V, ADC Value is 5/0.004887 = 1023 = 11111111 (binary)
• If
the input is 0.004887V, ADC Value is 0.004887/0.004887 = 1 = 00000001 (binary)
We require some hardware knowledge to program PIC
ADC in Hi-Tech C. If you don’t need hardware knowledge please skip this part
and go to Circuit Diagram.
ADC Module in Detail
Registers
PIC ADC has 4 registers
• ADCON0
– ADC Control Register 0
• ADCON1
– ADC Control Register 1
• ADRESH
– ADC Result High Register
• ADRESL
– ADC Result Low Register
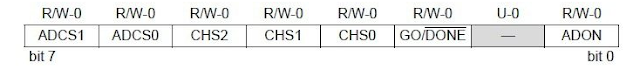
ADCON0 Register
ADCON0 Register – PIC 16F877A
• ADCS1
and ADCS2 are used to select A/D Conversion Clock. It should be selected in
accordance with device clock.
• CH2,
CH1 and CH0 are used to select one of the analog input channel out of eight
channels.
• GO/DONE
is the A/D Conversion Status bit. Setting this bit initializes A/D Conversion
and will be automatically cleared when the conversion is complete.
• ADON
is used to switch on/off the ADC Module. When it is 1, the ADC Module turns ON
and when it is 0, the ADC Module will be OFF.
ADCON1
Register
ADCON1 Register – PIC 16F877A
• ADFM
is the ADC Result Format select bit. Two 8 bit register (ADRESH and ADRESL) are
provided to store the 10-bit result of A/D Conversion, thus we need’t use 6
bits. When ADFM is 1, the result will be right justified, ie Most Significant
Bits of ADRESH will be read as 0. When ADFM is 0, the result will be left
justified, ie Least Significant Bits of ADRESL will be read as zero.
• ADCS2
is used to select A/D Conversion Clock in association with ADCS1 and ADC2 of
ADCON0 register.
• PCFG3
– PCFG0 are the A/D Port Configuration Control bits. Each pin amoung AN0 – AN7
is configured as analog, digital or reference voltage inputs according to the
status of these configuration bits as given below.
PIC ADC Port Configuration Bits
Note : TRIS Registers of Analog inputs must be
configured as input for the proper operation.
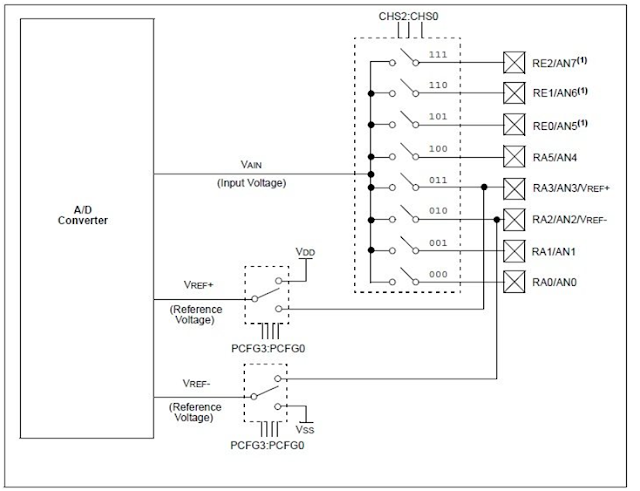
ADC
BLOCK DIAGRAM
ADC Module Block Diagram – PIC16F877A
Selection of A/D Conversion Clock
The time for A/D Conversion per bit is defined as
TAD and it requires minimum 12TAD to generate the 10-bit result. The time TAD
is determined by the A/D Conversion Clock which is software selectable to
following options.
• 2
TOSC
• 4
TOSC
• 8
TOSC
• 16
TOSC
• 32
TOSC
• 64
TOSC
• Internal
RC oscillator of ADC Module
TOSC is the time period of the device clock usually
provided by the crystal oscillator.
Care should be taken while selecting the A/D
Conversion Clock, such that the clock should provide the minimum TAD (1.6μS)
required for the correct A/D Conversion. So refer the following table before
setting the ADC clock.
ADC Clock Selection Table – PIC 16F877A
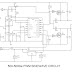
CIRCUIT
DIAGRAM
I am not going to explain deeply about the circuit. The reference voltages
of ADC is set to VDD (5V) and VSS (GND) though software (code given below).
Analog input is given to Channel 0 using a potentiometer, thus we can vary the
ADC input voltage from VSS to VDD. The 10-bit result of ADC is displayed using
10 LEDs, and 470Ω resistors are used to limit current through them.
SOFTWARE CODE
#include<htc.h>
#include<pic.h>
#define _XTAL_FREQ 8000000
void ADC_Init()
{
ADCON0 = 0x41; //ADC Module Turned ON and Clock is selected
ADCON1 = 0xC0; //All pins as Analog Input
//With reference voltages VDD and VSS
}
unsigned int ADC_Read(unsigned char channel)
{
if(channel > 7) //If Invalid channel selected
return 0; //Return 0
ADCON0 &= 0xC5; //Clearing the Channel Selection Bits
ADCON0 |= channel<<3; //Setting the required Bits
__delay_ms(2); //Acquisition time to charge hold capacitor
GO_nDONE = 1; //Initializes A/D Conversion
while(GO_nDONE); //Wait for A/D Conversion to complete
return ((ADRESH<<8)+ADRESL); //Returns Result
}
void main()
{
unsigned int a;
TRISB = 0x00; //PORTB as output
TRISC = 0x00; //PORTC as output
TRISA = 0xFF; //PORTA as input
ADC_Init(); //Initializes ADC Module
do
{
a = ADC_Read(0); //Reading Analog Channel 0
PORTB = a; //Lower 8 bits to PORTB
PORTC = a>>8; //Higher 2 bits to PORTC
__delay_ms(100); //Delay
}while(1); //Infinite Loop
}
#include<htc.h>
#include<pic.h>
#define _XTAL_FREQ 8000000
void ADC_Init()
{
ADCON0 = 0x41; //ADC Module Turned ON and Clock is selected
ADCON1 = 0xC0; //All pins as Analog Input
//With reference voltages VDD and VSS
}
unsigned int ADC_Read(unsigned char channel)
{
if(channel > 7) //If Invalid channel selected
return 0; //Return 0
ADCON0 &= 0xC5; //Clearing the Channel Selection Bits
ADCON0 |= channel<<3; //Setting the required Bits
__delay_ms(2); //Acquisition time to charge hold capacitor
GO_nDONE = 1; //Initializes A/D Conversion
while(GO_nDONE); //Wait for A/D Conversion to complete
return ((ADRESH<<8)+ADRESL); //Returns Result
}
void main()
{
unsigned int a;
TRISB = 0x00; //PORTB as output
TRISC = 0x00; //PORTC as output
TRISA = 0xFF; //PORTA as input
ADC_Init(); //Initializes ADC Module
do
{
a = ADC_Read(0); //Reading Analog Channel 0
PORTB = a; //Lower 8 bits to PORTB
PORTC = a>>8; //Higher 2 bits to PORTC
__delay_ms(100); //Delay
}while(1); //Infinite Loop
}
I hope you have gone through our previous tutorials.
STAY BLESSED
STAY BLESSED







No comments:
Post a Comment